Galital: The Digital Galaxy
⚠ WARNING: Work in progress content can change and it's not definitive.
Disclaimer:
Blockchain technologies are constantly evolving. This paper describes the best possible planned development, however due to the nature of the technology and the complexity of integrating the world of blockchain.
This document may be subject to change. We try to come as close as possible to the original plan, but sometimes modifications are necessary to improve the user experience and overcome technological barriers encountered during development.
1. Introduction
The digital divide began several years ago and the world is gradually becoming digitalized. The majority of payments are now made online and more and more digital products are being purchased. However, ownership of these goods rarely belongs to the buyers. The digital games that you have on your Steam account, PS store or others platforms do not really belong to you. The advent of NFTs (Non Fungible Tokens) has revolutionized digital goods and allows for true ownership within the blockchain. The NFTs belong to you and you are free to dispose of them as you want. However, the sale, purchase or exchange of NFTs is unfortunately not available to everyone yet. Between the difficulty of using the various marketplace and the increasing cost of gas fees, NFTs have become reserved for the medium and large wallet. With the arrival of utility NFTs (in video games for example) it has become crucial to transform the way we exchange NFTs to make them easily accessible to everyone, both in terms of usage and associated costs.
Galital was born out of this observation. An ecosystem to democratize the use of NFTs by creating an NFT platform based on Polkadot and the framework substrate. The development of Galital is based on several essential components:
The Factory
Making the creation and deployment of NFTs simple, fast and accessible to artists, content creators, video game creators or anyone else.
The Hub
Allow the interconnection of NFTs between different chains, whether it is to The Binance Chain, Ethereum, Avax, Polkadot or Flare, the goal of the Hub is to make the cross-chain transition simple and accessible.
The Market
Real main component of the ecosystem, the market allows the sale, purchase or exchange of NFTs, whether by auction or simple listing. Users also have the possibility to exchange NFTs directly. Finally, thanks to DeFi, the market allows NFTs to be borrowed and lent.
The Forge
The domain of Sharding. This is the place where the magic happens and allows the user to break their NFT into multiple sharded parts. This is also where you can reform an NFT with all its sharded parts.
The Vault
allows you to place your NFTs as collateral in order to retrieve tokens.
The Home
A dashboard to manage your NFTs.
2. Governance and Treasury
Galital is based on the substrate framework, so it benefits from a true decentralized governance system built directly within the blockchain itself. Among other things, it allows any $TAL holder to have a voice in the evolution of the ecosystem. Through governance, it is possible to submit proposals to help Galital evolve, submit bounty to direct the development of different products or even to offer tips to reward the work done by the community.
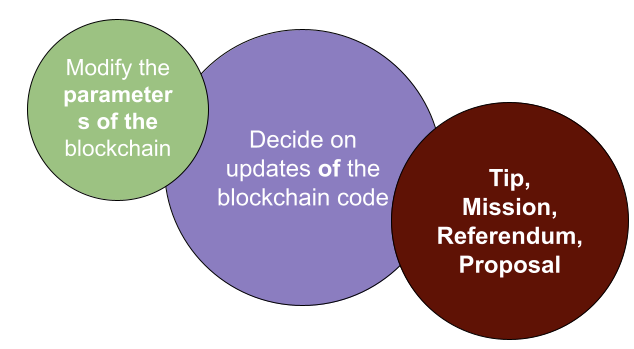
Governance is divided into 3 distinct groups:
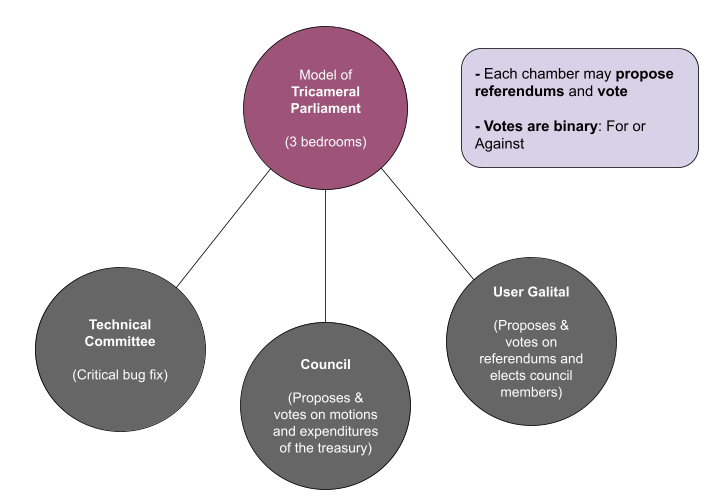
- The technical committee ensures the stability and safety of the blockchain. They are therefore able to submit emergency motions to council, once validated by the council, these motions apply in a shorter time frame than the classic motions. This chamber is reserved for members with an excellent knowledge of the blockchain and the Galital source code.
- Council members vote on motions and expenditures of the treasury (mission / tip). Their role is central and their mission is to make the ecosystem evolve by validating the proposals made by the community. They are elected by the community and their mandate currently lasts 7 days. The seats on the council are open and any $TAL holder can submit his candidacy.
- Holders of $TAL can vote to elect council members, make proposals to improve the blockchain, propose missions or carry out missions. They are the heart of Galital and it is thanks to them that the ecosystem evolves and moves forward.
It is thanks to this governance system that Galital users can have a strong impact in the evolution of the ecosystem. It is no longer a single entity that has the power, but the entire community. In order to support the different evolutions of the blockchain, the treasury is a crucial mechanism allowing Galital to support itself without the help of a third party. It essentially allows the community to be able to set up remunerated missions to develop new products, do marketing, add new bridges or any other proposal deemed relevant by the members of the board and validated by the community.
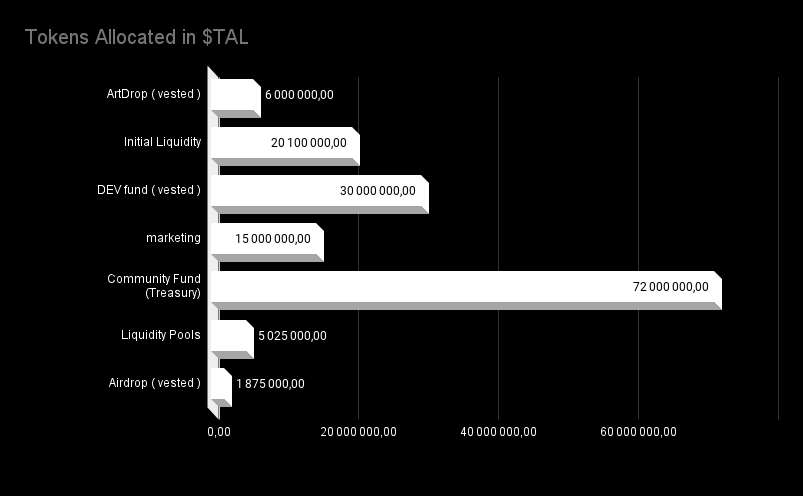
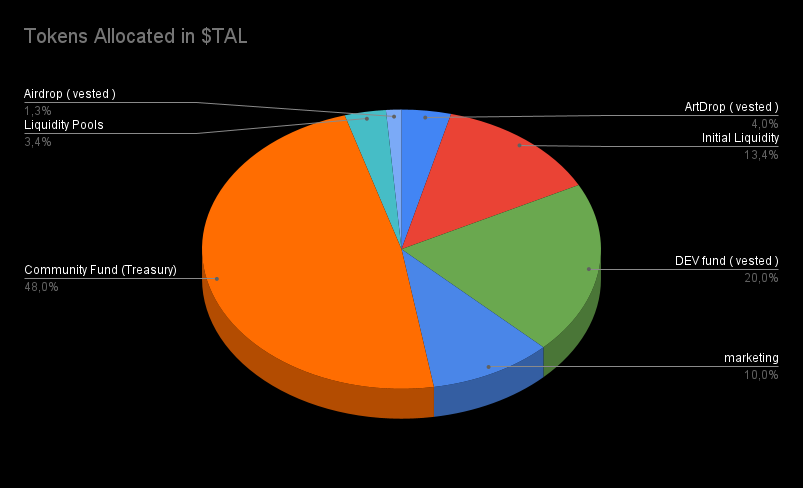
3. Initial tokens allocation
4. Placement and security of the chain (Staking)
Any holder of $TAL can participate in the staking to secure the blockchain. In return for this contribution, staker will receive $TAL rewards. There are 2 distinct roles: Validator and Nominator .
4.1 Validator
Validator secure the chain by locking $TAL and processing blocks and transactions, they are backed by a stake from the validator owner and the nominater that stake on top of the validator.
These will play a crucial role in the addition of new blocks to the relay chain and, by extension, to all secondary chains. This will allow the parties to carry out inter-chain transactions via the relay chain.
Validator have 2 functions:
- They verify the information contained in an assigned set of blocks from substrings to determine their validity (such as the identity of the parties to the transaction and the subject matter of the contract).
- They participate in consensus mechanisms to produce the building blocks of the chain based on the validity statements of the other validator.
In the case of non-compliance with the consensus algorithms, the validator is slashed by removing some or all of the $TAL locked on it. This mechanism thus helps to discourage bellicose actors. Conversely, respect and good performance are rewarded by the blockchain.
There are currently 500 places available for validator. In order to be elected by the network and thus create new blocks, validator must be in the first 500 in terms of $TAL blocked (validator + nominations). If a validator is not elected by the network, they will not do any work and will not receive any reward.
In return for their contribution, validators receive the block rewards (new $TAL created, based on the inflation system provided by the network) as well as 20% of the transaction fee (the rest going to the treasury). These rewards are divided between the validator and its nominators according to their respective shares (minus the commission set by the validator to cover maintenance costs).
4.2 Nominator
The nominators are responsible for designating their participation to the validators. By locking their $TAL on validators, they allow validators to be selected by the network to create new blocks and share the associated rewards and penalties.
While validators are active participants in the network who take part in the production and finality mechanisms of the blocks, nominators play a more passive role with a delegation approach. Therefore, there is no need for technical knowledge or specific equipment. However, a good nominator is wise with regard to the validators he or she chooses, paying attention to his or her own reward percentage and the risk of being sanctioned if the validator acts in a belligerent manner. Nominators are rewarded according to the number of shares they hold in the Validator (less commission fees).
5. The Factory
The factory is an essential component of the Galital ecosystem, it allows, among other things, to create and deploy its own NFTs in a simple and fast way. Thanks to an ergonomic interface design, creating NFTs becomes child's play and within everyone's reach. Whether you're an artist, content creator, Video game developer or passionate about NFTs, the factory is made to simplify your life and save you precious time, allowing you to create endless NFTs in a snap of your fingers.
It will also be possible, during the creation of an NFT, to choose a % of royalties that will be paid to the creator for each transaction of the said NFT in the Galital market. This system will provide creators with an additional income incentive to share their creations.
6. The Hub (Bridges between chains + IU)
The Hub is the dedicated space for cross-chain bridges. This is where users will be able to transfer their NFTs between the different channels supported by Galital (the list will evolve according to the choices of the community). Initially, transfers to and from Ethereum, BSC, Avalanche, Polkadot, Matic and Flare will be available. This will allow the user to freely transfer their NFTs for direct use in the Galital ecosystem, including the market. The transfer and flow is simple, the user will have a graphical user interface where they can select the origin and destination chain for the transfer of NFTs or tokens, the user then signs the transaction through the network of oracles (Galital will use ChainSafe technology), and transfers the assets to the desired chain.
7. The Market
The market is Galital's central point, this is where users will be able to buy or sell NFTs. The strength of the market is its simplicity of use and diversity, it will be possible for the seller to choose the crypto he wants to receive as payment and the buyer will be able to pay in the crypto of his choice, thanks to an integrated DEX system, the purchases will be fluid, no more time to convert your ETHs into DAI because the NFT of your choice was only listed in DAI. No more exorbitant gas fees, your purchase is now done in one click and you can then buy your NFTs whenever you want, quickly and easily.
At the time of a sale, 2 expenses are deducted from the sale:
- Market Fees: 2.5%.
- Creator’s Fees : defined by the creator when creating the NFT.
The market fee can be reduced when paying in $TAL as well as in possession of special NFTs. Cumulatively they can even reach a reduction of 100%. However, the creator's fee cannot be reduced.
Users also have the possibility to make a private sale (NFT can only be purchased through the address specified by the seller). In this case, only the fees for the creator are deducted.
8. The Vault
The vault is the ideal place to stack NFTs to farmer new tokens. Whether you want to earn in-game coins or other crypto tokens, the vault allows you to lock your NFTs for a period of time to make them work for you.
9. Fractional NFT System
Galital intends to implement fractional NFT in order to push the NFT beyond the limit and unlock a bunch of new possibilities.
Fractional Ownership
Fractional NFT allows users to share ownership of NFT’s. You want an epic sword in a game but you can afford it ? Or maybe a Cryptopunk catches your eyes but it’s way too expensive to buy one on your own ?
Fractional NFT will allow you to take a share on these NFT’s. It’s even more useful when you want to take advantage of DeFi with NFT. Fractional NFT unlocks you the ability to take fractional part in order to receive an income with the lending system for instance. You will benefit from all the DeFi associated with NFT’s.
Fractional NFT system has so many opportunities way beyond this paper. If you’re a mmo gamer, you will definity want to use it to buy NFT as a guild and share ownership between members. Even further, game developers could develop smart contracts that allow guilds to own an NFT and share it with the guild members according to their rank. Thanks to this, you will now can own NFT as a guild, rent it or sell it and the benefit will be shared between all the members. Or you can also simply share an NFT with your friends or your community and use it in game one at the time.
This system is a huge step forward for the gaming industry and allows a lot of opportunities to play, own and earn together.
Market Price Discovery
Sharding will also unlock a better and healthier price discovery for NTFs. Shared parts will be directly driven by the market and traded like any token. If a user wants to take the full ownership of an sharded NFT, it will need to get all the shard parts in order to transform them into the NFT. You can also at any time break an NFT into any shard you want. That allows you to give more scarcity to a single NFT.
10. The forge
The forge is the place where users can break their NFT’s into shards. They decide the scarcity (10 shards, 100, 1000 eg...) Then, they can distribute or sell it on the market place like a token. This will unlock the possibility of video game creators to improve the scarcity of their NFT and allow a greater number of people to get into it.
When you have collected all the shards from an NFT, you can go on the forge and fuse them in order to retrieve the original NFT.
11. Lending / Borrow
In addition to greatly simplifying the buying and selling of NFTs, the market also allows users to rent or lend their NFTs. Want to get a valuable item in a game for a certain period of time? Do you own lands that you would like to make available? A friend needs an NFT in your possession temporarily? The market will allow you to perform all these actions and much more in a simple and secure way. No more need to send your NFT in order to lend it. A new field of possibilities opens up for you with the Galital market.
12. The Home
The home acts as a dashboard to manage your NFTs. This is where you will be able to view your NFTs, managing your assets is your main control panel. From here you will be able to manage all applications, create tokens, buy/sell on the marketplace.
13. INK! Contracts
Since Substrate supports Wasm smart contracts, this means that any language that can compile to Wasm can be used to write these contracts. ink! is Parity's answer to writing smart contracts using the Rust programming language.
ink! is an integrated domain specific language (eDSL) based on Rust for writing intelligent Wasm contracts specifically for "Pallet Contracts". The main objectives of INK! are user-friendliness, conciseness and efficiency.
13.1 Contract Components
ink! should feel familiar to developers who have programmed using other modern intelligent contract languages. The skeleton of a contract with all the same components you would expect:
- Events
- Storage space
- Deployment function (manufacturer)
- Public functions
- Internal functions
In ink! mutability and visibility are explicitly defined by contract function. In these functions, you have access to a number of common Substrate types such as AccountId, Scales, Hash, etc.
In addition, you have access to commonly used environment variables such as caller ID and more!
13.2 Design
The main objectives of ink! are accuracy, conciseness and efficiency.
inking! is designed to be as close as possible to the Rust programming language. The language uses attribute macros to mark up standard Rust structures into understandable contract components.
Because ink! follows Rust standards, tools like rustfmt and rust-analyzer already work natively.
13.3 Overflow security
Being written in Rust, INK! can provide over/underrun security at compile time. Using a Rust compiler configuration, you can specify whether you want to support mathematical overflows or whether you want contract execution to panic in the event of an overflow. There is no need to continually import "Safe Math" libraries, although Rust also offers built-in verified, encapsulated, and saturated mathematical functions.
Note: There are known issues with the functionality of the compiler overflow checks and the resulting size of the blob Wasm object. This feature may change or be repeated in the future.
13.4 Test environment
INK! provides an integrated test environment that can be used to perform out-of-chain unit testing with the Rust framework. This makes it simple and easy to ensure that your contract code works as expected, without the need for third-party test platforms.
13.4 ink! vs Solidity
Rust is an ideal intelligent contract language. It is secure, memory-safe, and free of undefined behaviors. It generates small binary files because it doesn't include extra bloat, such as a garbage collector, and advanced optimizations and removes dead code. Using compiler flags, Rust can automatically protect itself against integer overflow.
INK! chooses not to invent a new programming language, but rather to adapt a subset of Rust to serve this purpose.
As a result, you benefit from all the tools and support available free of charge for the Rust ecosystem. In addition, as the language grows, INK! will automatically have access to new features and functionality, improving the way you can write smart contracts in the future.
Here is a brief comparison of the features between INK! and Solidity:
| ink! | Solidity | |
| Virtual Machine | Any Wasm VM | EVM |
| Encoding | Wasm | EVM Byte Code |
| Language | Rust | Standalone |
| Overflow Protection | Enabled by default | None |
| Constructor Functions | Multiple | Single |
| Tooling | Anything that supports Rust | Custom |
| Versioning | Semantic | Semantic |
| Has Metadata? | Yes | Yes |
| Multi-File Project | Planned | Yes |
| Storage Entries | Variable | 256 bits |
| Supported Types | Docs | Docs |
| Has Interfaces? | Planned (Rust Traits) | Yes |